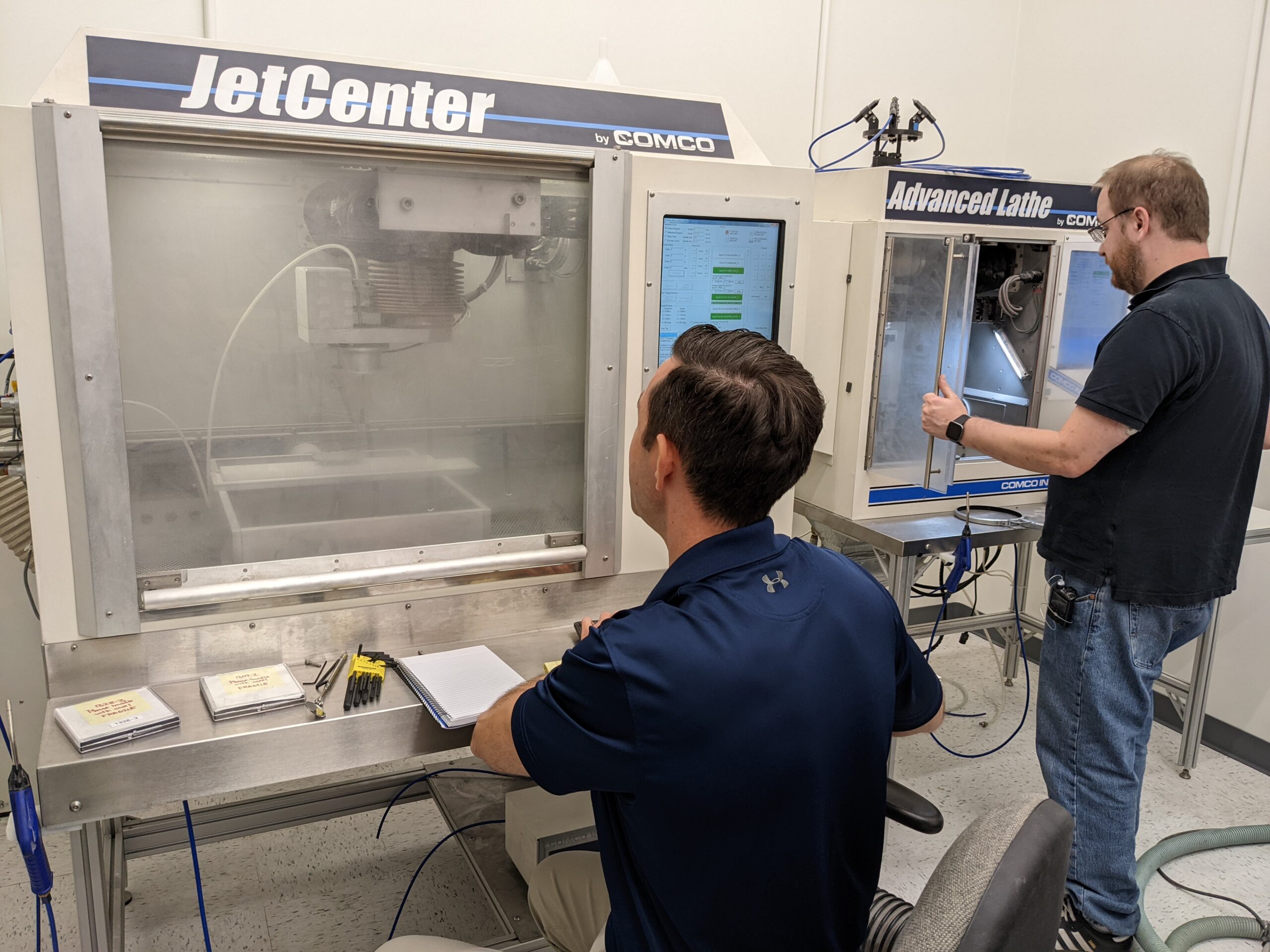
Case Studies
Wire Stripping? Get Uniform Removal + Sharp Delineation with the Ring Nozzle
YOUR MISSION: WIRE STRIPPING
(SHOULD YOU CHOOSE TO ACCEPT IT)
- Remove PTFE coating in multiple, evenly-spaced 2″ sections from a stainless wire.
- The delineation from coating to clean wire should be <0.005″.
Your materials to complete this mission:
- a manual Comco MicroBlasting system.
- one able-bodied operator.
- 100 pieces of ss wire, half of which are 86” in length, the other half 43”.ODs are 0.020” and 0.016” respectively.
Ok. This task is not usually considered a “mission”; but it is a common challenge for the manufacturers in the medical industry and applicable to anyone working with PTFE wire or coil, PEEK tube, Nitinol tube, stainless tube, and needles.
It also allows us to have a little fun while we shamelessly plug a handy-dandy addition to your blasting system that will save time, money, sanity; and most importantly, help you complete this mission with speed, precision, and accuracy.

Before You Blast
We catalog PTFE coating removal under the umbrella of “Coating Removal“. While abrasive jet machining is the process of carefully removing layers of one type of material to carve channels or features; selective cleaning is the process of selectively removing unwanted material to reveal another. Often, selective cleaning involves the removal of one type of material from another type—like, a ductile layer from a brittle, or vice versa.
Abrasive selection is key to successful selective cleaning because it often involves two different materials. For this mission, a gentle abrasive like sodium bicarbonate can remove the top polymer layer without damaging the underlying wire.
The Single Nozzle Option
Now that you have your abrasive, the task seems relatively straightforward, right?
- Fixture your nozzle.
- Feed the wire through the blast cabinet to the starting point.
- Press the footswitch and blast.
- Turn the wire and blast again.
- Slide the wire to the next point and repeat.
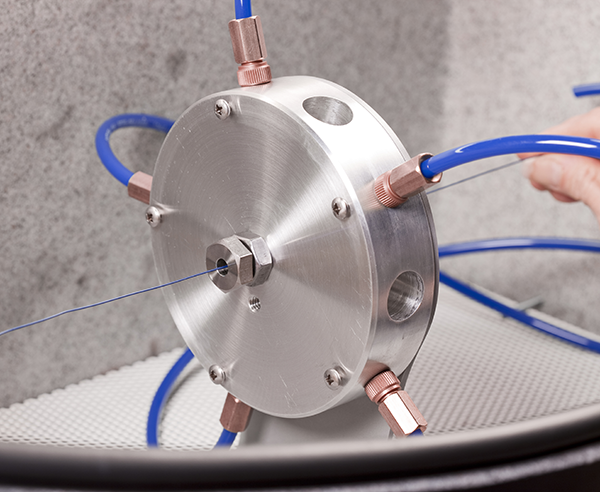
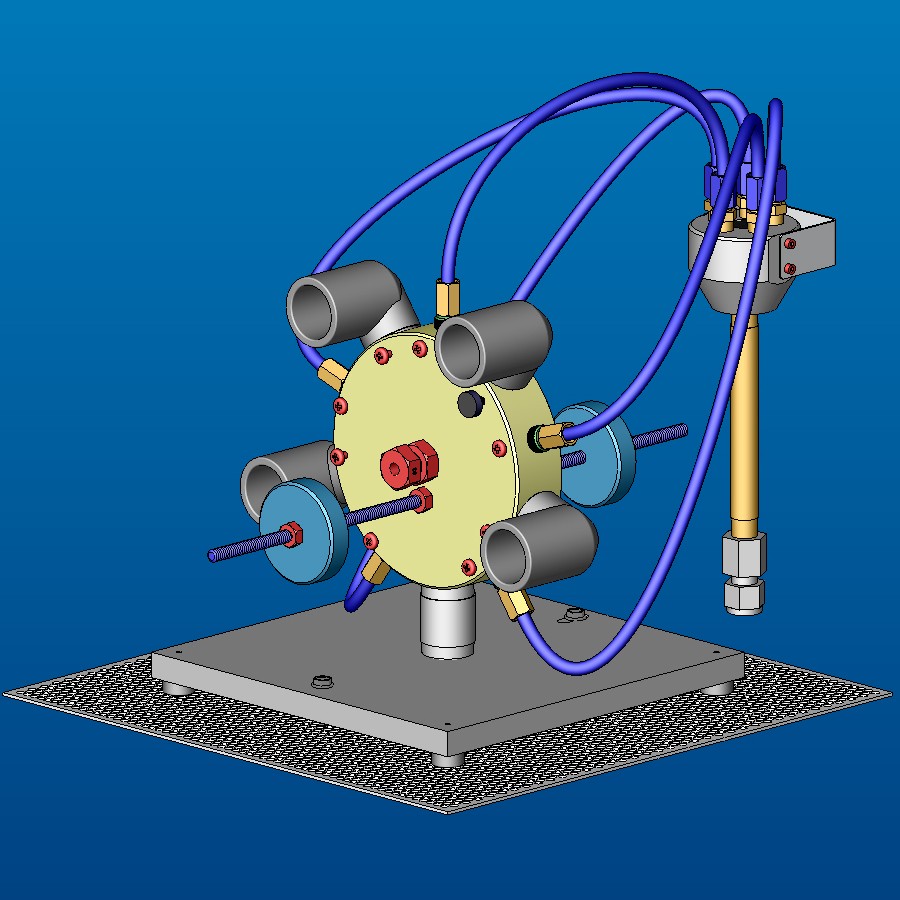
What is the Ring Nozzle?
The Ring Nozzle consists of three major components: the Ring Nozzle, a splitter, and two guide bolts.
Ring Nozzle
Configured with five MB2520-30 Hi/Performance nozzles (custom options available); the nozzle array assembly is designed to spread the abrasive flow uniformly over a circular cross-section.
Splitter
The splitter divides a single abrasive stream from your blaster into multiple uniform abrasive streams.
Guide Bolts
Guide bolts ensure the part is fed through the center of the blast stream and provide a masking feature when a part requires only partial blasting. Opening sizes are available from 0.020″ to 0.125″. Screwing the bolts in or out adjusts the length of the blast region. Stop wheels are used for stop points for the blasted part and ensure a repeatable blast position and length. The standard stop rod is 6″ (152 mm long), but longer stop rods are available upon request.
To Recap:
Q: What has 5 nozzles and blasts uniformly 360° on a targeted part to a sharp delineation?
A: The Ring Nozzle.
Q: How sharp is that delineation?
A: <0.005″.
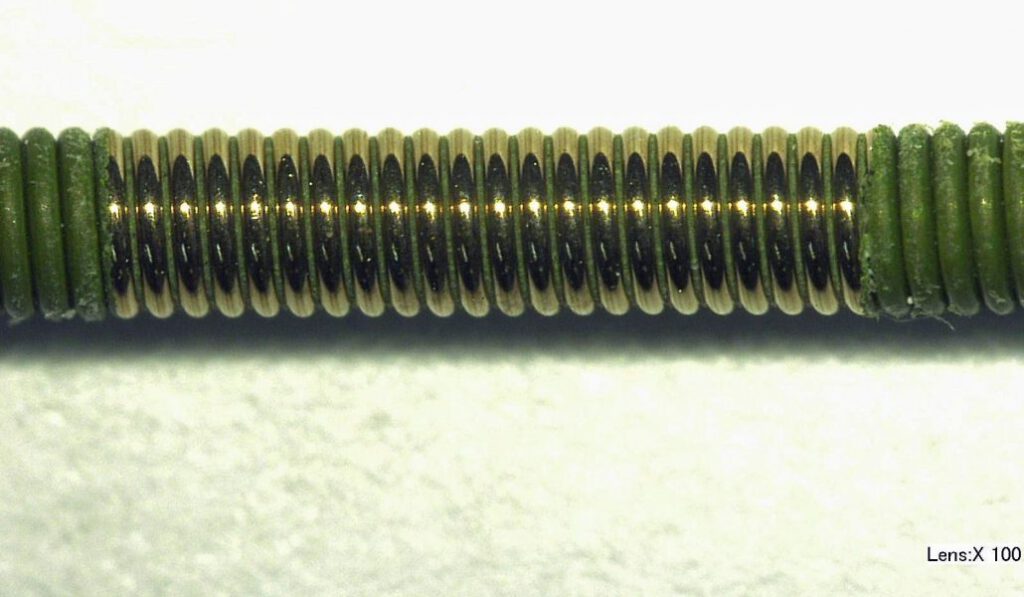
Q: What do results look like on other materials?
A: See below:
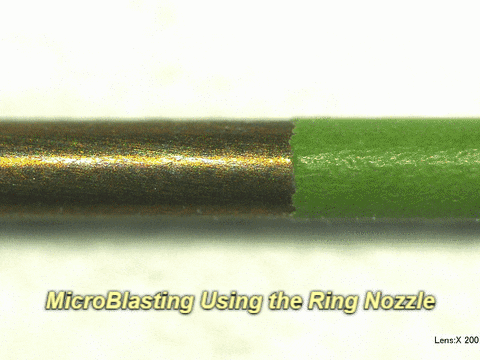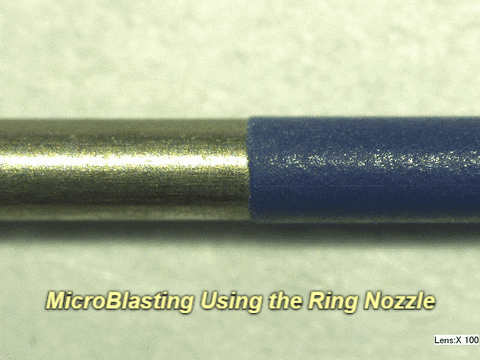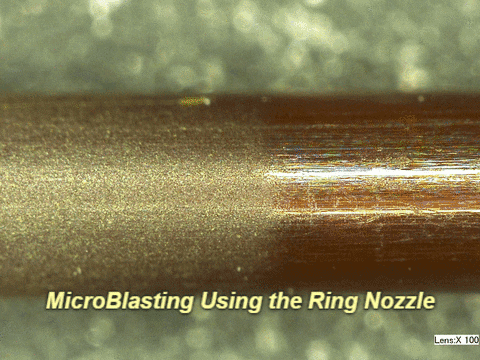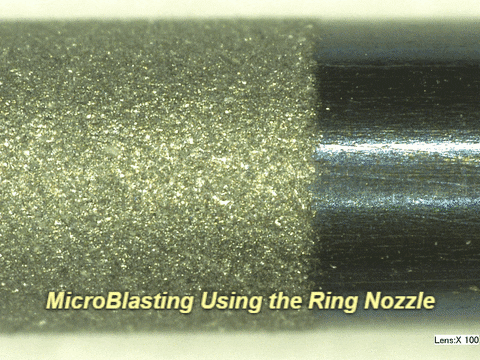
Q: Who successfully completed this mission?
A: You did. (Don’t worry, this screen will not self-destruct.)
Applications Lab
Let our experts help find the right solution for your part. We know no two applications are the same. Our Technical Specialists manage sample-part testing and processing from start-to-finish. They actively collaborate with our Sales and Engineering Teams while remaining completely accessible to you throughout the process.




